
Gingival recession and Treatment
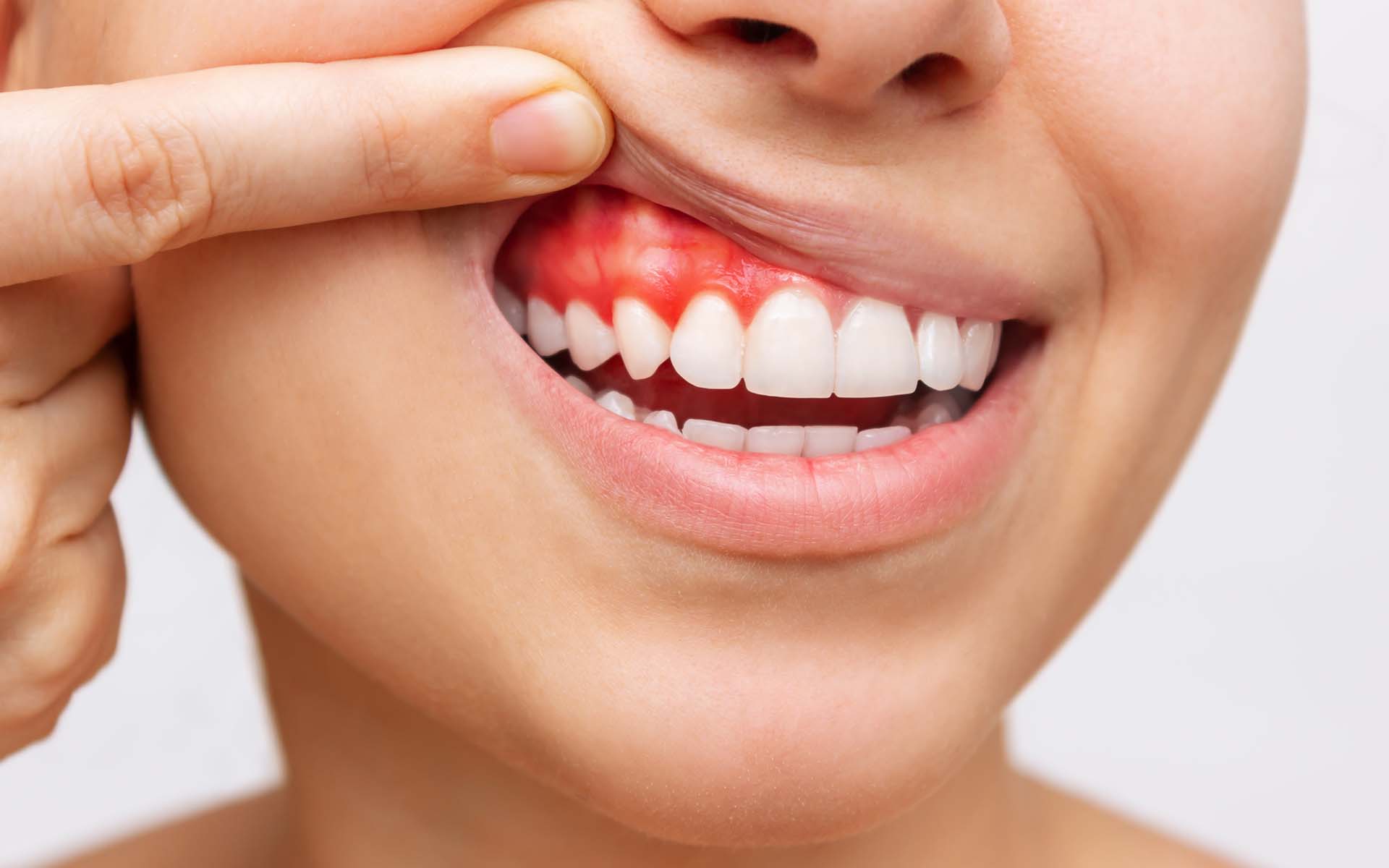
Gingival recession or periodontitis is a serious infectious gum disease that damages the soft tissue around the teeth and weakens the gums. If gingival recession is not treated, the bones that support the teeth can be irreversibly destroyed. The first sign of weak gums is often tooth sensitivity. In addition, teeth that appear longer than normal are among the symptoms. In the last case, if it is not treated, tooth losses and tooth weekning are seen.
What Causes gingival recession?
Although this disease caused by infection is very common and yet it is a preventable disease. Improper implementation of general oral and dental care routines can cause this disease. Making hard movements while brushing teeth, not choosing the appropriate toothbrush and neglecting the use of dental floss cause plaque formation. Plaques cause gingivitis, and gingivitis causes weakening of the gums and all these resulting in recession. Gingivitis can be reversed with early diagnosis, professional intervention and proper oral hygiene, thus preventing gingival recession. In addition to these, natural processes caused by aging can weaken the gums. Moreover;
- Drugs that cause dry mouth
- Malnutrition and vitamin C deficiency
- Diabetes
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause
- Diseases that adversely affect the immune system, such as AIDS, cancer, and leukemia.
- To smoke
- Obesity Such reasons can also cause periodontitis, gingival recession"
What are the Symptoms of gingival recession ?
A healthy person's gums are hard and pale pink in color and fit snugly around the teeth. Various symptoms are observed in the gums with periodontitis;
- Dark red or even turning purple, raised or swollen gums
- Gaps formed between teeth and gums, spaces between teeth
- Bleeding from teeth while brushing teeth
- Sensitive gums
- Loosening of teeth and recession of gums
- Teeth appearing longer than normal
- Bad breath (halitosis)
In cases where gum recession is suspected, it is necessary to see a dentist without wasting time. If treated early, gingival recessions can be treated without causing tooth loss. Visiting the dentist regularly and having routine check-ups is the most important way to prevent diseases before they begin.
Gingival Recession Treatment
Treatment methods are determined by specialist dentists according to the degree of progression of the disease. If there is an initial situation, surgical treatment is not needed. Treatment is completed with invasive procedures, medication and simple devices. Tartar and bacteria are cleaned from pockets around the teeth with laser or ultrasonic devices or scraping. Since bacteria and tartar will settle more easily on a rough root surface, smoothing the root surfaces is one of the methods to prevent the formation of bacteria. Tropical antibiotics and antibiotic mouthwashes are among the treatments that will prevent the formation of bacteria. It may also be recommended to use oral antibiotics to completely destroy the bacteria that cause infection in gingival recession.
In case of progressive gingival recession, dental surgery will come into play.
- Flap Surgery: It is a surgery that is considered suitable for the reduction of gingival pockets. Small cuts are made into the gums and some of the gum tissue can be pushed back. With this method, it is aimed to perform a more effective bacterial cleaning and root arrangement.
- Soft Tissue Graft Practice: Diş etlerindeki hasar görmüş yumuşak dokuların onarılması ve güçlendirilmesi esasına dayanır. For this purpose, the required amount of tissue is taken from the patient's plate or another suitable donor area. The removed tissue is transferred to the damaged gum tissue. With this treatment, gingival recession is reduced, tooth roots exposed as a result of recession are covered, and your teeth are provided with a more aesthetic appearance.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: In this treatment method, regrowth of the bone damaged by bacteria is achieved. In order to achieve this, a special fabric biological fabric is placed between the bone and the tooth by the dentist. The biological fabric blocks the entry of unwanted soft tissue to allow bone regrowth. This provides the time needed for the bone to repair itself.
- Tissue Stimulating Gel Practice: The tissue stimulating gel practice is based on the injection of tissue stimulating protein gels into the diseased tooth root. This gel, which is created by imitating the structure of proteins that support the development of tooth enamel, ensures the growth of healthy bone tissue.